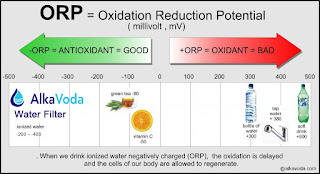
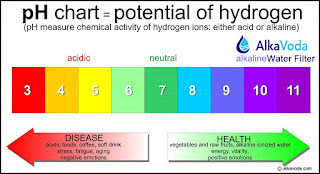
Dangers Of Chlorine In Your Water

What is Chlorine? Chlorine is a disinfectant added to drinking water to reduce or eliminate microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses, which can be present in water supplies. The addition of chlorine to our drinking water has greatly reduced the risk of waterborne diseases. If you’ve ever been to a swimming pool, and most of us have, you’ll recognize that distinct chemical chlorine smell from the pool water. Most swimming pools use chlorine to disinfect the water and keep any bacteria or algae from growing, but that chemical also has tremendous adverse affects on our health. Why Is Chlorine So Dangerous? Chlorine was used in it’s gaseous form as a chemical poison weapon during World War I, and the results were disastrous. Today, chlorine is used in swimming pools, household cleaning supplies, and water treatment plants that end up as our drinking water. At room temperature, chlorine turns into a gas that is easily inhaled which can cause a myriad of health problems, so